
I want to start with something I’ve been seeing across the industry for the past several years. Organizations are struggling with their AI initiatives, and the root cause often has nothing to do with their models, their data scientists, or their algorithms. The problem is architectural, and it starts with how we’ve been thinking about databases.
Yesterday, Oracle officially released Oracle AI Database 26ai for on-premises Linux x86-64 platforms. This isn’t just another version bump. This release represents a fundamental shift in how we should be thinking about the relationship between databases and artificial intelligence. And honestly? It’s about time.
Let me explain why this matters to you as a database administrator.
The Fragmentation Problem Nobody Wants to Talk About
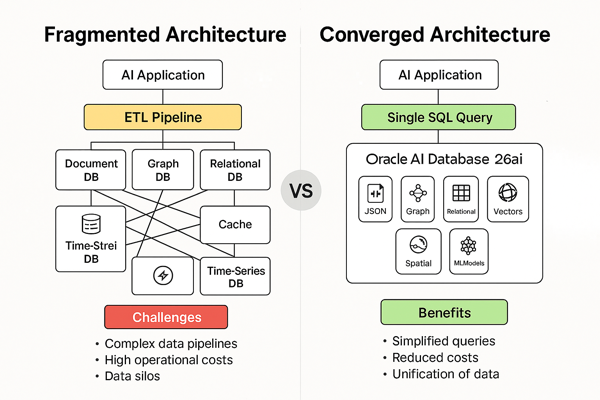
Over the past decade, our industry went through what I call the “database fragmentation era.” The thinking was simple: specialized tools for specialized problems. Need to store documents? Use a document database. Graph relationships? There’s a database for that. Time-series data? Yet another platform. And now with AI, vector databases have entered the conversation.
On paper, this made sense. Each tool was genuinely excellent at its specific use case. But here’s what I’ve observed working with enterprises across multiple industries: that fragmentation comes with a hidden tax that’s now coming due.
I’ve walked into organizations running ten, fifteen, sometimes more different database platforms. Each one has its own security model, backup procedures, monitoring infrastructure, patching cycles, and skill requirements. Your team isn’t just managing databases anymore; they’re managing a complex integration ecosystem.
And here’s where it gets interesting for AI. Your AI models need data from multiple sources, often in real time. When that data lives in fifteen different places, you’ve got a serious problem. Data scientists end up spending 70-80% of their project time on data engineering rather than actual machine learning. That’s not a technology problem – that’s an architecture problem. Yea, tools like Oracle GoldenGate can minimize so of the fragmentation; but it should be viewed as a tool to enhance your AI strategy by getting data into the correct unified platform.
Enter the Converged Database
Oracle has been building toward what they call a “converged database” for years, and the strategic rationale has never been stronger than it is right now.
What exactly is a converged database? Think of it like a smartphone. Before smartphones, you carried separate devices for different functions. A phone for calls. A camera for pictures. A GPS for navigation. An iPod for music. Each device did its job well, but carrying all of them was cumbersome, and they didn’t work together seamlessly.
The smartphone converged all these capabilities into a single device. Suddenly, you could take a picture and immediately share it over the data connection. The individual capabilities became more powerful because they could work together within a unified platform.
That’s what Oracle’s converged database approach delivers for data management. You can store relational data alongside JSON documents, graph relationships, spatial coordinates, and now vector embeddings – all within the same database instance. These aren’t bolted-on features; they’re native capabilities that leverage Oracle’s decades of investment in query optimization, transaction management, and security.
Why 26ai Changes the Game
Oracle AI Database 26ai brings over 300 new features with a heavy focus on artificial intelligence capabilities. But here’s what makes it significant for those of us managing data infrastructure:
- Native Vector Data Types. Vectors are now first-class citizens in the database. You can define columns with vector types, index them for fast similarity search, and query them using distance functions. This isn’t a third-party extension – it’s integrated into the core query engine.
- Unified Data Access. Your AI model needs to query customer data, transaction history, product information, and user behavior patterns. In a fragmented architecture, that means coordinating queries across multiple databases and dealing with latency between systems. In a converged database, it’s a single query engine with ACID transactions.
- Real-Time Data Freshness. AI models trained on stale data produce stale insights. When your data pipeline involves copying data between multiple specialized databases, you introduce lag. Every hop adds latency. A converged database eliminates most of these hops – your operational data and your AI-ready data can live in the same place.
- Integrated Security. When your vectors, documents, relational data, and AI models all live in the same database, they’re all protected by the same security infrastructure. Row-level security, virtual private database, data redaction, encryption – all the enterprise security features you already know apply consistently across all your data.
What This Means for You
So what does this mean for database administrators looking at an AI-transformed landscape?
- Your existing skills are more valuable than ever. If you’ve invested years in understanding Oracle database internals, that investment continues to pay dividends. The AI capabilities build on the same foundation you already know – SQL, optimization, security, high availability, backup and recovery. You’re not starting from scratch; you’re extending your expertise into new territory.
- You need to think architecturally. The technical skills matter, but so does the ability to evaluate trade-offs and make strategic recommendations. When a development team asks for a specialized vector database, you need to be equipped to have a substantive conversation about the alternatives. Your value is in helping them think through the decision.
- You need to understand AI fundamentals. You don’t need to become a data scientist, but you need to speak the language. When someone asks you to optimize vector index performance, you need to understand what vectors are, why similarity search matters, and what trade-offs are involved.
The Bottom Line
The database is no longer just where you store your data. It’s becoming the foundation for how your organization leverages artificial intelligence. The release of Oracle AI Database 26ai for on-premises deployment marks a significant milestone in this evolution.
For those of us who’ve built our careers around data management, this is an opportunity. AI is transforming every industry, and the foundation for AI transformation is data. Your expertise in managing, securing, and optimizing that data puts you at the center of that transformation.
In the next post in this series, we’ll dive into many of the items related to this evolutional change to our roles. Until then, I’d love to hear your thoughts. How is your organization approaching the convergence question? Drop a comment below or reach out directly.
Bobby Curtis

I’m Bobby Curtis and I’m just your normal average guy who has been working in the technology field for awhile (started when I was 18 with the US Army). The goal of this blog has changed a bit over the years. Initially, it was a general blog where I wrote thoughts down. Then it changed to focus on the Oracle Database, Oracle Enterprise Manager, and eventually Oracle GoldenGate.
If you want to follow me on a more timely manner, I can be followed on twitter at @dbasolved or on LinkedIn under “Bobby Curtis MBA”.
