The Evolution of Oracle GoldenGate Automation: From Command Line to AI-Driven Intelligence
When I started working with Oracle GoldenGate years ago (2011ish), managing replication environments meant one thing: a lot of time at the command line. Every status check, every configuration change, every troubleshooting session required SSH access, GGSCI commands, and manual coordination across multiple servers. It worked, but it was time-consuming and prone to human error.
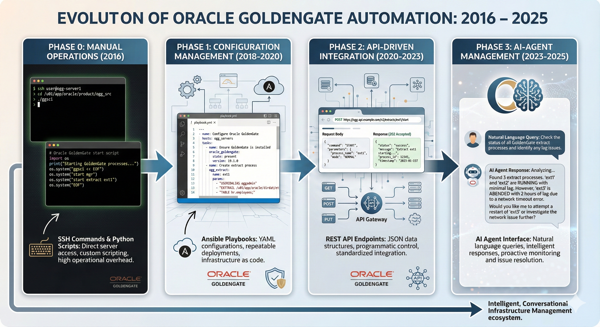
Here’s what I’ve learned over the years: Oracle’s commitment to improving GoldenGate hasn’t just been about adding features—it’s been about fundamentally changing how we interact with and manage replication environments. Since the release of Oracle GoldenGate 12.1.0.1 in August 2017, which introduced the Microservices Architecture, Oracle set a clear objective: make the product easier and more accessible for end users.
That commitment has transformed GoldenGate from a command-line tool into a cloud-ready, API-driven platform that’s enabling dynamic replication architectures years ahead of the competition. Let me walk you through this evolution—from manual SSH sessions to AI-powered management—and show you how automation capabilities have improved with each phase.
Phase 0: The SSH Era – Making the Command Line Work for Us
Timeline: Pre-2017
Automation Method: Python Fabric over SSH
Key Challenge: Managing multiple GoldenGate environments efficiently
In the early days, if you managed Oracle GoldenGate across multiple environments, you lived in SSH sessions. Need to check status on three servers? That’s three SSH logins and three sets of GGSCI commands. Need to verify replication lag across your entire infrastructure? Better clear your calendar.
I remember looking at different tools to simplify this process, initially experimenting with Perl for network commands. The breakthrough came when I discovered Fabric—a Python-based tool for streamlining SSH application deployments. If it could deploy applications, I reasoned, it could certainly help with basic GoldenGate monitoring.
The approach was straightforward: create Python scripts that could SSH into multiple servers simultaneously and execute GGSCI commands. Here’s what that looked like:
from fabric.api import *
env.hosts = [
'source-server.company.com',
'target-server.company.com'
]
env.user = "oracle"
def info_all():
with cd("$OGG_HOME"):
run("echo info all | ./ggsci")
With a single command (fab info_all), I could check the status of GoldenGate processes across multiple servers. What used to take 15 minutes of repetitive work was now accomplished in 30 seconds.
What This Taught Us: Automation didn’t have to be complicated. Even basic scripting over SSH could deliver significant time savings and reduce human error. More importantly, it showed that there was a better way to manage GoldenGate—we just needed the right tools.
Limitations: While effective, this approach had clear boundaries. You were still essentially automating manual commands. Configuration management remained manual, and any changes required careful coordination across environments.
Phase 1: Configuration Management – Ansible Brings Structure
Timeline: 2017-2021
Automation Method: Ansible playbooks for deployment and configuration
Key Advancement: Repeatable, version-controlled installations
When Oracle GoldenGate 12.1 introduced the Microservices Architecture, it opened up new possibilities for automation. But installation and configuration were still time-consuming processes. This is where Ansible changed the game.
Ansible brought enterprise-grade configuration management to GoldenGate deployments. Instead of manually installing binaries, configuring environments, and setting up directory structures, we could define everything in playbooks and execute repeatable deployments across multiple servers.
At RheoData, we built standardized Ansible templates for GoldenGate 21c that reduced installation time from hours to minutes. The approach used three key components:
Variable Definitions defined everything from installation paths to software versions:
stage_dir: /opt/software/
ogg_home: /opt/app/oracle/product/19.1.0/oggcore_21c
ogg_deployment_home: /opt/app/oracle/gg_deployment
gg_services_software: 213000_fbo_ggs_Linux_x64_services_shiphome.zipTask Orchestration managed the complete installation process:
- Create required directory structures
- Copy installation binaries and response files
- Extract Oracle Client libraries
- Install GoldenGate Microservices
- Configure environment variables
- Set up credentials and certificates
Automation Scripts complemented the installation:
- Password management utilities
- Self-signed certificate generation
- Service Manager control scripts
- NGINX configuration for web access
The result? A fully functioning GoldenGate 21c environment deployed in a fraction of the time it used to take, with consistent configurations across all environments.
What This Changed: Ansible transformed GoldenGate from an art form into a repeatable engineering process. Teams could deploy consistent environments, version control their configurations, and integrate GoldenGate installation into CI/CD pipelines. This was the foundation for treating GoldenGate infrastructure as code.
The Evolution in Thinking: We moved from “how do we automate commands?” to “how do we automate entire environments?” This shift in perspective set the stage for what came next.
Phase 2: The RESTful Revolution – APIs Change Everything
Timeline: 2017-2024
Automation Method: RESTful APIs and JSON-based orchestration
Key Breakthrough: Programmatic control without command-line access
This is where Oracle GoldenGate’s evolution really accelerated. The Microservices Architecture didn’t just change how GoldenGate was deployed—it fundamentally changed how we could interact with it. Every function that was available through AdminClient or the web interface became accessible via REST APIs.
For those of us who’d been managing GoldenGate for years, this was revolutionary. Suddenly, we could start, stop, configure, and monitor replication processes from anywhere using standard HTTP requests. No SSH required. No command-line interface needed. Just clean, well-documented APIs.
Starting and Stopping Processes
The most basic operations—starting and stopping extracts and replicats—became trivially simple. Instead of logging into servers and executing GGSCI commands, we could use a JSON file and a cURL command:
{
"$schema": "ogg:command",
"name": "start",
"processName": "SALES_EXT",
"processType": "extract"
}curl -u oggadmin:password \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X POST \
http://localhost:16001/services/v2/commands/execute \
-d @start_extract.jsonThe response came back in structured JSON, providing immediate confirmation of success or detailed error information if something went wrong.
Dynamic Configuration Updates
Even more powerful was the ability to modify parameter files without touching the server. Need to add a new table to replication? No problem. Build a JSON payload with the complete parameter file content and PATCH it through the API:
{
"config": [
"extract SALES_EXT",
"useridalias SALES_DB domain OracleGoldenGate",
"exttrail aa",
"table SALES.ORDERS;",
"table SALES.ORDER_ITEMS;",
"table SALES.CUSTOMERS;",
"table SALES.NEW_TABLE;"
]
}The API validated the configuration, reported any errors, and applied the changes—all without restarting processes unnecessarily.
Initial Load Automation
Perhaps the most impressive advancement was in initial load operations. Traditionally, adding new tables to an existing replication stream required data pump exports, network transfers, imports, and careful coordination of extract and replicat processes. The process could take days.
With the REST APIs, we could automate file-based initial loads through a series of orchestrated API calls:
- Create a special extract for initial load
- Configure it to capture specific tables
- Generate trail files with the initial data
- Create corresponding replicat processes
- Apply the data to target tables
- Merge the tables into the ongoing replication stream
What used to be a multi-day project became a scripted operation that could complete in hours—or even minutes for smaller datasets.
What This Enabled: REST APIs didn’t just make automation easier—they made it more reliable and reproducible. Teams could build sophisticated orchestration scripts, integrate GoldenGate with monitoring platforms, and create self-service portals for common operations. The automation was no longer limited by SSH access or command-line interfaces.
The Competitive Advantage: While other replication tools were still tied to proprietary interfaces and manual processes, Oracle GoldenGate’s API-first approach enabled dynamic replication architectures. Need to spin up new replication streams in response to business requirements? Build it with APIs. Need to integrate with cloud orchestration platforms? APIs make it possible. This flexibility put GoldenGate years ahead of competitive solutions.
Phase 3: Intelligent Automation – AI Agents Enter the Picture
Timeline: 2025 and Beyond
Automation Method: AI agents using Model Context Protocol
Key Innovation: Natural language interaction with complex systems
Now we’re entering territory that seemed like science fiction just a few years ago. The question isn’t “can we automate this task?” but rather “can we make the system intelligent enough to understand what we need and figure out how to do it?”
This is where AI agents—specifically those using the Model Context Protocol (MCP)—are changing the game. Instead of writing scripts to perform specific tasks, we’re building intelligent assistants that can understand natural language questions and interact with GoldenGate environments to provide meaningful answers.
The Problem We’re Solving
Even with all the automation improvements through Phase 2, managing GoldenGate still required deep technical knowledge. You needed to know which API endpoints to call, how to interpret the responses, and what actions to take based on what you found. New team members faced a steep learning curve, and troubleshooting still required experienced DBAs.
How AI Agents Work
The breakthrough with MCP is that it provides a standardized way for AI models to securely access live information from your systems. Unlike traditional AI training approaches, MCP allows AI to:
- Access real-time status information through REST APIs
- Interpret complex responses in context
- Correlate information across multiple processes
- Provide insights in natural language
The technical implementation connects an AI agent to GoldenGate’s REST APIs through a secure MCP server:
class GoldenGateAgent:
async def get_process_status(self, process_type):
"""Get real-time status for extracts or replicats"""
url = f"http://{self.host}:{self.port}/services/v2/{process_type}"
response = await self._secure_api_call(url)
return self._format_for_ai(response.json())
@mcp.tool()
async def check_replication_health():
"""Analyze overall replication environment health"""
extracts = await agent.get_process_status("extracts")
replicats = await agent.get_process_status("replicats")
return agent.analyze_health(extracts, replicats)
What It Looks Like in Practice
Instead of running multiple commands and correlating results manually, you can now have conversations with your GoldenGate environment:
You: “Give me a status update on all replication processes”
AI Agent: “I found 8 extract processes and 6 replicats running. All extracts are operating normally with lag times under 5 seconds. However, ORDERS_REP replicat is showing 45 seconds of lag—significantly higher than the typical 10-second average. The process is still RUNNING, but this warrants investigation. Would you like me to check the target database for potential bottlenecks?”
The agent isn’t just reporting status—it’s providing context, identifying anomalies, and suggesting next steps.
Real-World Applications
The practical benefits extend beyond simple status checks:
- Faster Troubleshooting: What used to require 20-30 minutes of digging through logs and status commands is now a 5-minute conversation. The AI helps pinpoint issues quickly so you can focus on resolution.
- Proactive Monitoring: Instead of scheduled checks that might miss developing issues, you can ask broad questions like “anything unusual happening?” and get intelligent summaries that highlight potential problems.
- Knowledge Transfer: New team members can learn by asking questions in plain English rather than memorizing AdminClient commands and API syntax. The AI becomes a teaching tool that helps people become productive faster.
- Pattern Recognition: AI agents excel at spotting trends that humans might miss—like gradual increases in lag that could indicate developing problems, or correlations between different processes that suggest systemic issues.
Security and Trust
Let me be clear about something: implementing AI agents requires careful consideration of security. The approach we’ve developed at RheoData ensures:
- AI never accesses actual replicated data—only metadata and status information
- All connections use proper authentication with no hardcoded credentials
- The MCP server runs within your network perimeter
- Every AI interaction is logged for audit purposes
- Sensitive configuration details remain in your systems, not in AI models
The Future of Management: AI agents represent a fundamental shift in how we think about infrastructure management. Instead of learning commands and APIs, operators can focus on understanding business requirements and system behavior. The technical complexity is still there, but it’s hidden behind an intelligent interface that makes expertise more accessible.
The Bigger Picture: Why This Evolution Matters
Over these four phases, Oracle GoldenGate has evolved from a command-line tool requiring deep technical expertise into a platform that combines enterprise-grade capabilities with increasingly accessible management interfaces. This progression hasn’t been random—each phase built on what came before, addressing real operational challenges while maintaining the robustness that enterprises require.
Enabling Dynamic Replication Architectures
The most significant impact of this evolution is how it’s enabled entirely new approaches to data replication. When every operation requires manual coordination, replication architectures tend to be static. You design them carefully, implement them cautiously, and change them reluctantly.
But when automation spans from deployment through operation to intelligent management, replication becomes dynamic. Need to add new tables to replication? Deploy new replication streams for a new application? Respond to changing data latency requirements? These aren’t multi-week projects anymore—they’re operational tasks that can be executed quickly and reliably.
This capability puts Oracle GoldenGate years ahead of competing solutions. While other tools are still catching up to basic REST API functionality, GoldenGate environments are being managed by AI agents that understand context and provide intelligent guidance.
From Operations to Strategy
Perhaps more importantly, this evolution is shifting how technical teams spend their time. Instead of focusing on the mechanics of replication—the command syntax, the configuration details, the manual monitoring—teams can focus on strategic questions:
- How can we use real-time data to create business value?
- What replication architectures best support our cloud migration strategy?
- How do we ensure data consistency across hybrid environments?
- What’s the optimal balance between replication performance and system resources?
The technical complexity hasn’t disappeared—it’s been abstracted and automated, allowing experienced professionals to operate at a higher level while making it easier for newer team members to contribute effectively.
Looking Forward: What’s Next?
Based on the trajectory of these four phases, where is GoldenGate automation heading? Here’s what I see coming:
- Self-Healing Systems: AI agents that don’t just identify problems but can execute corrective actions automatically, with human oversight for critical operations.
- Predictive Operations: Machine learning models that analyze historical patterns to predict issues before they occur—proactive rather than reactive management.
- Intent-Based Configuration: Describing what you want to achieve in business terms and having the system figure out the technical implementation details.
- Seamless Cloud Integration: GoldenGate replication that adapts automatically to cloud-native architectures, from Kubernetes to serverless platforms.
- Cross-Platform Intelligence: AI agents that understand not just GoldenGate but the entire data ecosystem, correlating replication behavior with database performance, application patterns, and business metrics.
Practical Takeaways: Applying These Lessons
If you’re managing Oracle GoldenGate environments today, here’s how to think about this evolution:
- Start Where You Are: You don’t need to jump directly to AI agents. Each phase builds on the previous one. If you’re still mostly manual, start with basic scripting or Ansible automation. Already automated? Explore the REST APIs more deeply.
- Build Incrementally: Don’t try to automate everything at once. Pick one frequent operational task and automate it well. Then move to the next. Small wins build momentum and demonstrate value.
- Document What Works: As you automate, capture what you learn. Create runbooks, document API patterns, and share scripts with your team. This knowledge becomes valuable when you’re ready for the next phase.
- Think in Layers: Each automation layer should make the one above it possible. SSH automation enables consistent deployments. Consistent deployments enable API-based orchestration. API orchestration enables AI-powered intelligence.
- Security First: As automation increases, so do the potential impacts of errors or security breaches. Build proper authentication, logging, and approval workflows into your automation from the beginning.
Conclusion: A Journey Worth Taking
The evolution of Oracle GoldenGate automation from Phase 0’s SSH scripts to Phase 3’s AI agents represents more than just technical progress—it’s a fundamental shift in how we approach data replication management. What started as a way to save time on repetitive tasks has become a comprehensive strategy for managing complex, dynamic replication architectures.
Oracle’s commitment since the Microservices Architecture release in 2017 has been clear: make GoldenGate easier to use while maintaining the enterprise-grade reliability that organizations depend on. They’ve delivered on that promise, and in doing so, they’ve created a platform that’s genuinely ahead of the competition.
For those of us who’ve been in this industry for decades, watching this evolution has been remarkable. We’ve gone from spending hours on basic operational tasks to having intelligent conversations with our infrastructure about how to optimize and improve it.
The question isn’t whether to embrace this evolution—it’s how quickly you can apply these automation capabilities to deliver more value for your organization. The tools are there, the path is proven, and the benefits are real.
Bobby Curtis

I’m Bobby Curtis and I’m just your normal average guy who has been working in the technology field for awhile (started when I was 18 with the US Army). The goal of this blog has changed a bit over the years. Initially, it was a general blog where I wrote thoughts down. Then it changed to focus on the Oracle Database, Oracle Enterprise Manager, and eventually Oracle GoldenGate.
If you want to follow me on a more timely manner, I can be followed on twitter at @dbasolved or on LinkedIn under “Bobby Curtis MBA”.
